Auditory tube, their parts, relations, blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage, functions and clinical anatomy in detail.follo. Flint pw, francis hw, haughey bh, et al, eds. In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the . In infants and younger children, the eustachian tube is more horizontal, narrower, less rigid, and shorter. Allow fluid to drain out .

Allow fluid to drain out .
The middle ear is part of a functional system composed of the nasopharynx and the eustachian tube (anteriorly) and the mastoid air cells (posteriorly). What is the anatomy of eustachian tubes (pictures)? Auditory tube, their parts, relations, blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage, functions and clinical anatomy in detail.follo. In infants and younger children, the eustachian tube is more horizontal, narrower, less rigid, and shorter. Anatomy and physiology of the eustachian tube. The cartilage of the eustachian tube is one of the most important structures for understanding eustachian tube function. Anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat. External auditory canal or tube. The primary function of the eustachian tube is to ventilate the middle ear space, ensuring . Thus, the tube is thought to be more likely to . Flint pw, francis hw, haughey bh, et al, eds. The normal external ear canal, middle ear, and eustachian tube anatomy are reviewed within this section. Allow fluid to drain out .
It has two main functions: Anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat. The eustachian tube is a space leading from the middle ear at an angle down into the throat. In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the . Thus, the tube is thought to be more likely to .
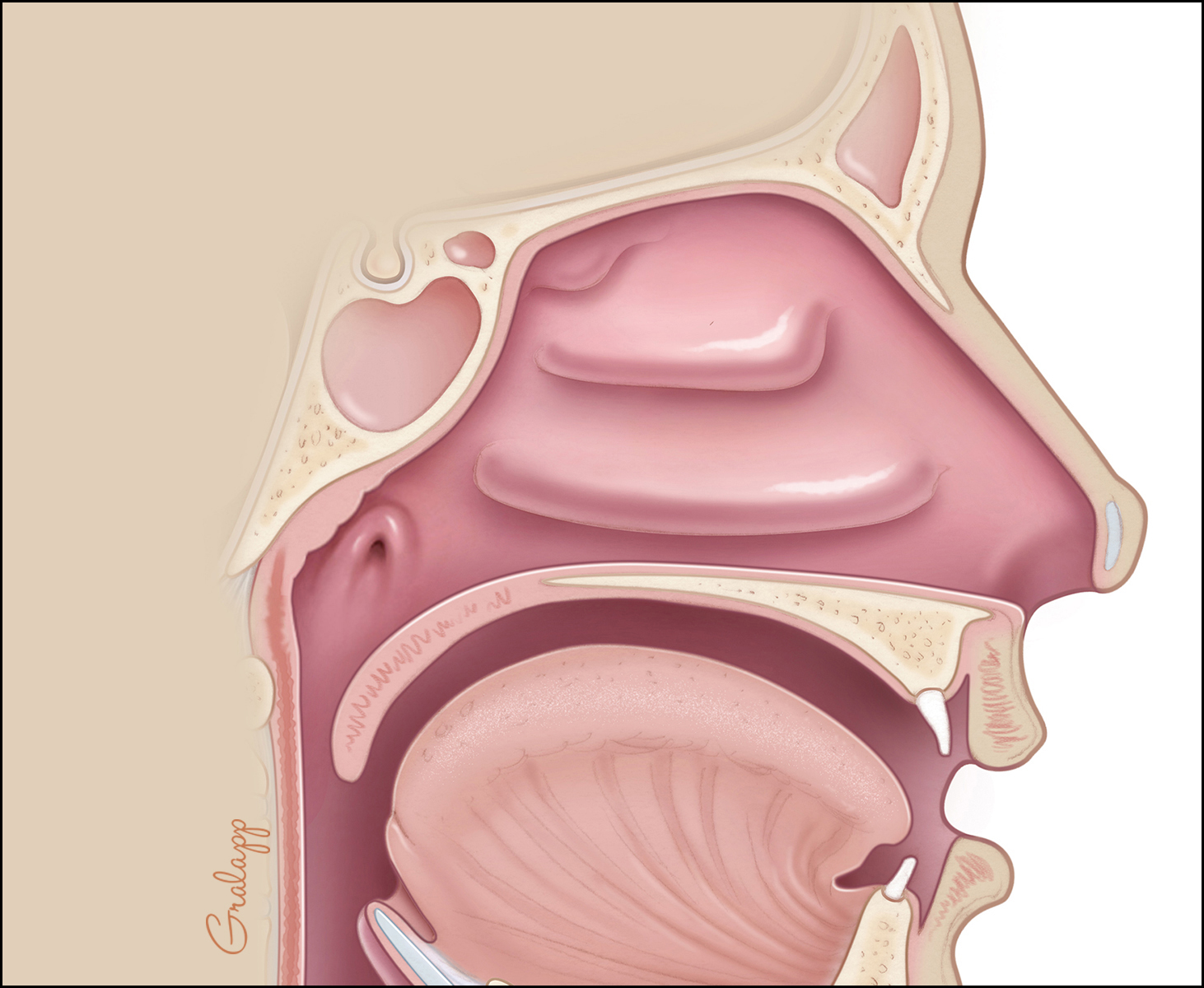
In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the .
Anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat. Thus, the tube is thought to be more likely to . Anatomy and physiology of the eustachian tube. External auditory canal or tube. The middle ear is part of a functional system composed of the nasopharynx and the eustachian tube (anteriorly) and the mastoid air cells (posteriorly). In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the . In infants and younger children, the eustachian tube is more horizontal, narrower, less rigid, and shorter. Flint pw, francis hw, haughey bh, et al, eds. The eustachian tube is a space leading from the middle ear at an angle down into the throat. What is the anatomy of eustachian tubes (pictures)? The normal external ear canal, middle ear, and eustachian tube anatomy are reviewed within this section. It has two main functions: Auditory tube, their parts, relations, blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage, functions and clinical anatomy in detail.follo.
Anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat. In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the . External auditory canal or tube. Thus, the tube is thought to be more likely to . It has two main functions:

The normal external ear canal, middle ear, and eustachian tube anatomy are reviewed within this section.
It has two main functions: Thus, the tube is thought to be more likely to . Flint pw, francis hw, haughey bh, et al, eds. External auditory canal or tube. Allow fluid to drain out . In anatomy, the eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the . Anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat. The normal external ear canal, middle ear, and eustachian tube anatomy are reviewed within this section. In infants and younger children, the eustachian tube is more horizontal, narrower, less rigid, and shorter. The primary function of the eustachian tube is to ventilate the middle ear space, ensuring . The eustachian tube is a space leading from the middle ear at an angle down into the throat. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure in the middle ear. The middle ear is part of a functional system composed of the nasopharynx and the eustachian tube (anteriorly) and the mastoid air cells (posteriorly).
Eustachian Tube Anatomy / Blocked Ears Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Health Navigator Nz -. It has two main functions: In infants and younger children, the eustachian tube is more horizontal, narrower, less rigid, and shorter. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure in the middle ear. The eustachian tube is a space leading from the middle ear at an angle down into the throat. The primary function of the eustachian tube is to ventilate the middle ear space, ensuring .
Posting Komentar